Automation & Future Workplace
Understanding the automation and how it impacts the future workplace
Cedric-Pascal Sommer, Ying Li, Manav Sahani, Kevin Gao

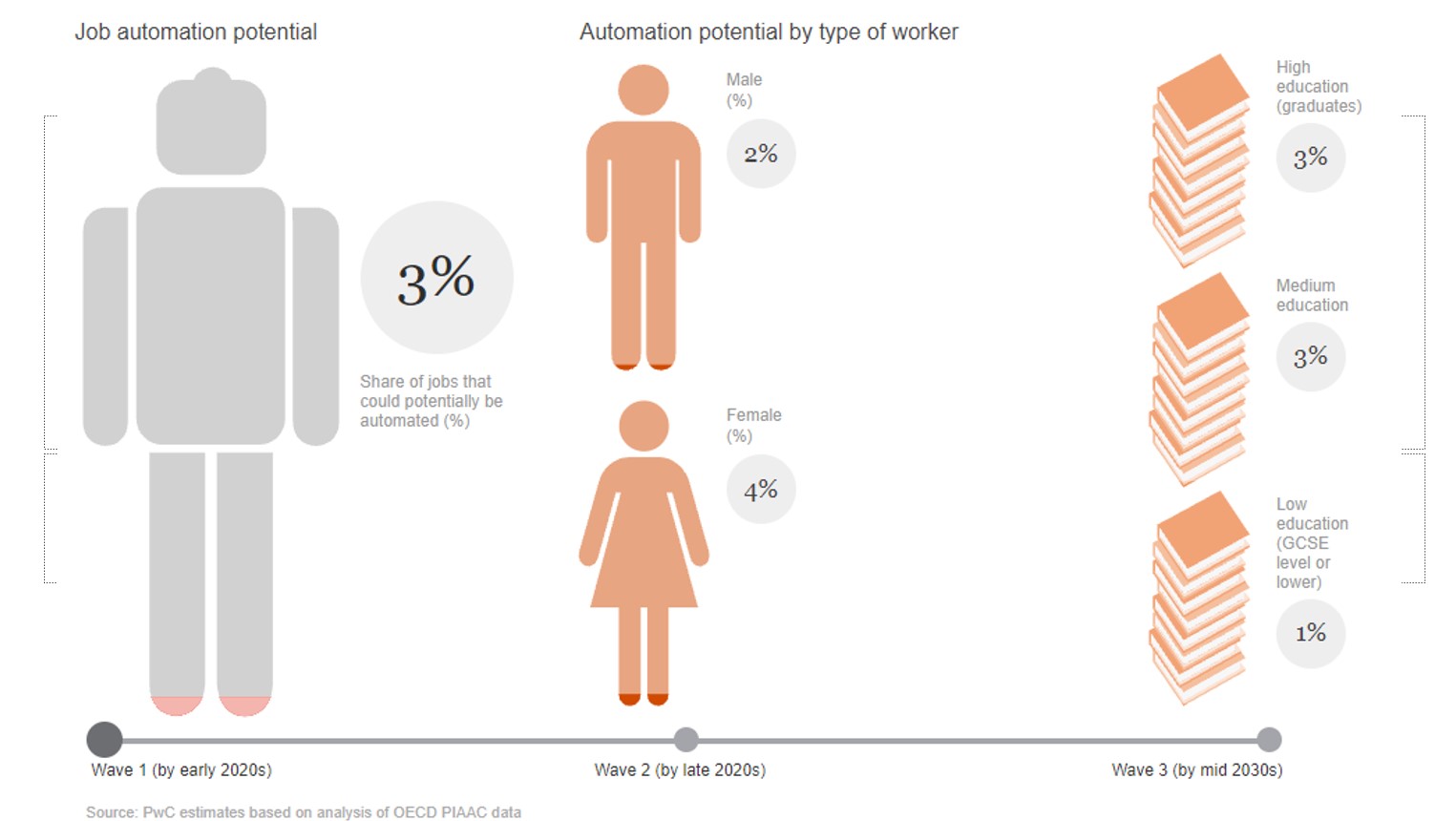
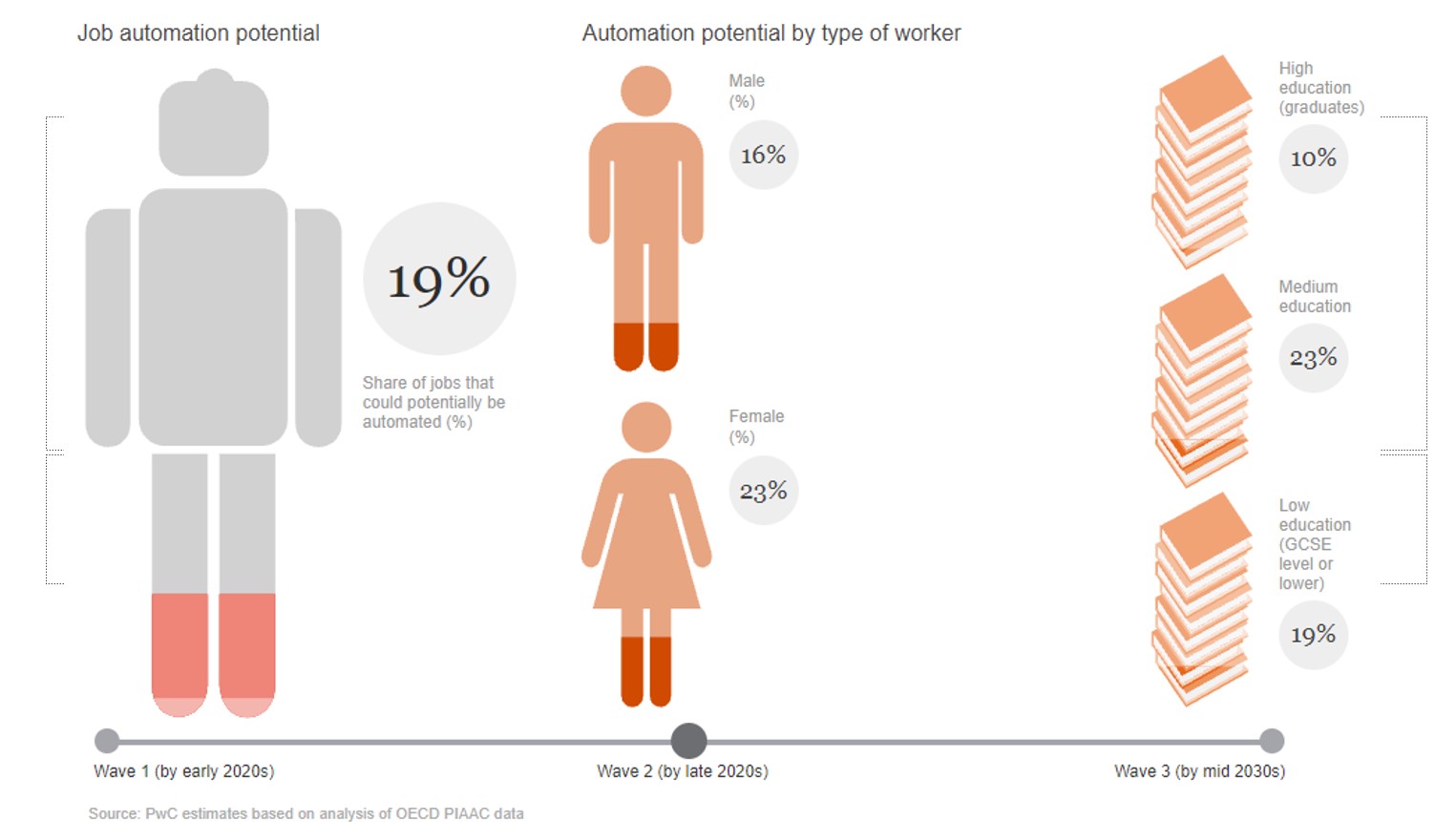
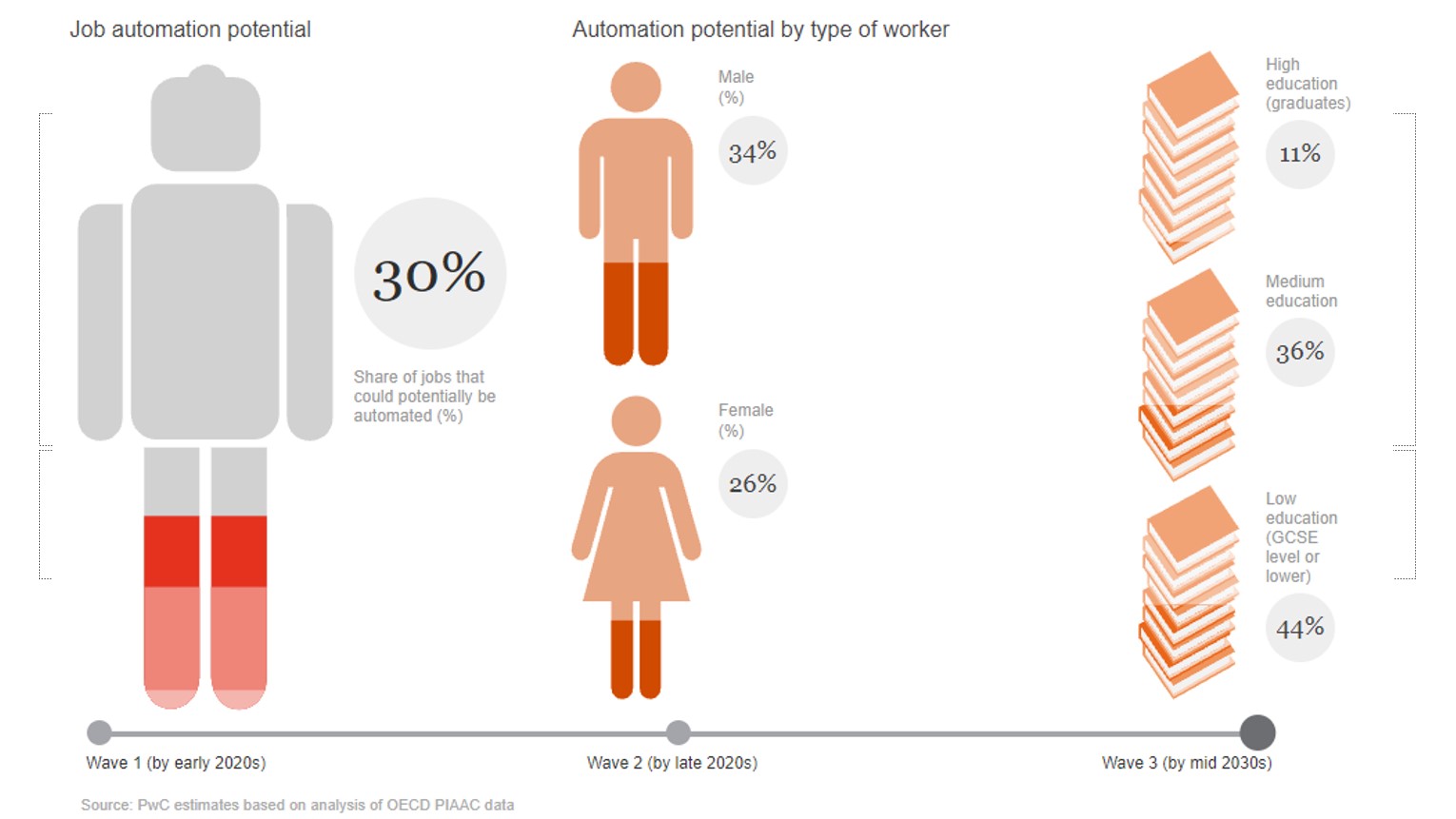

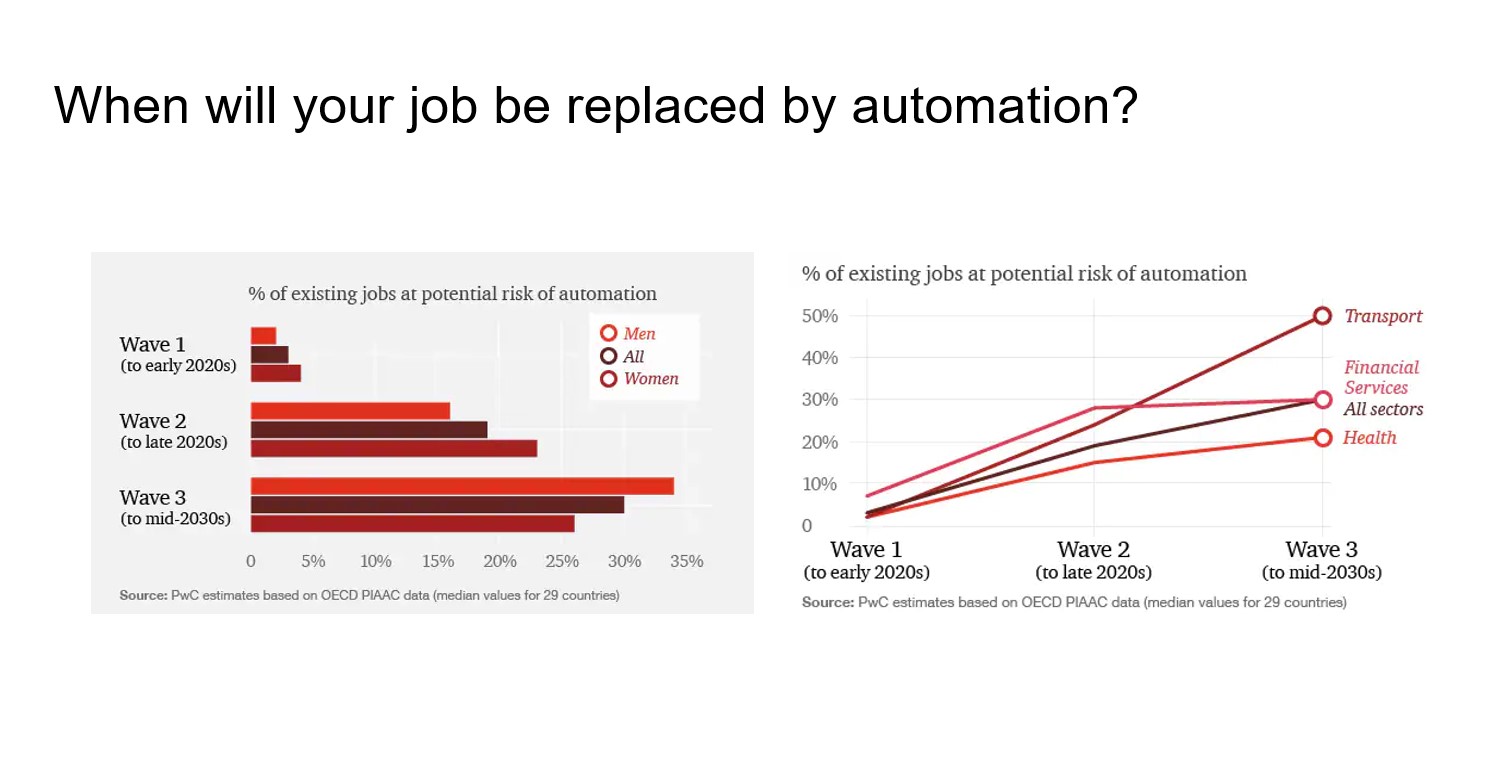


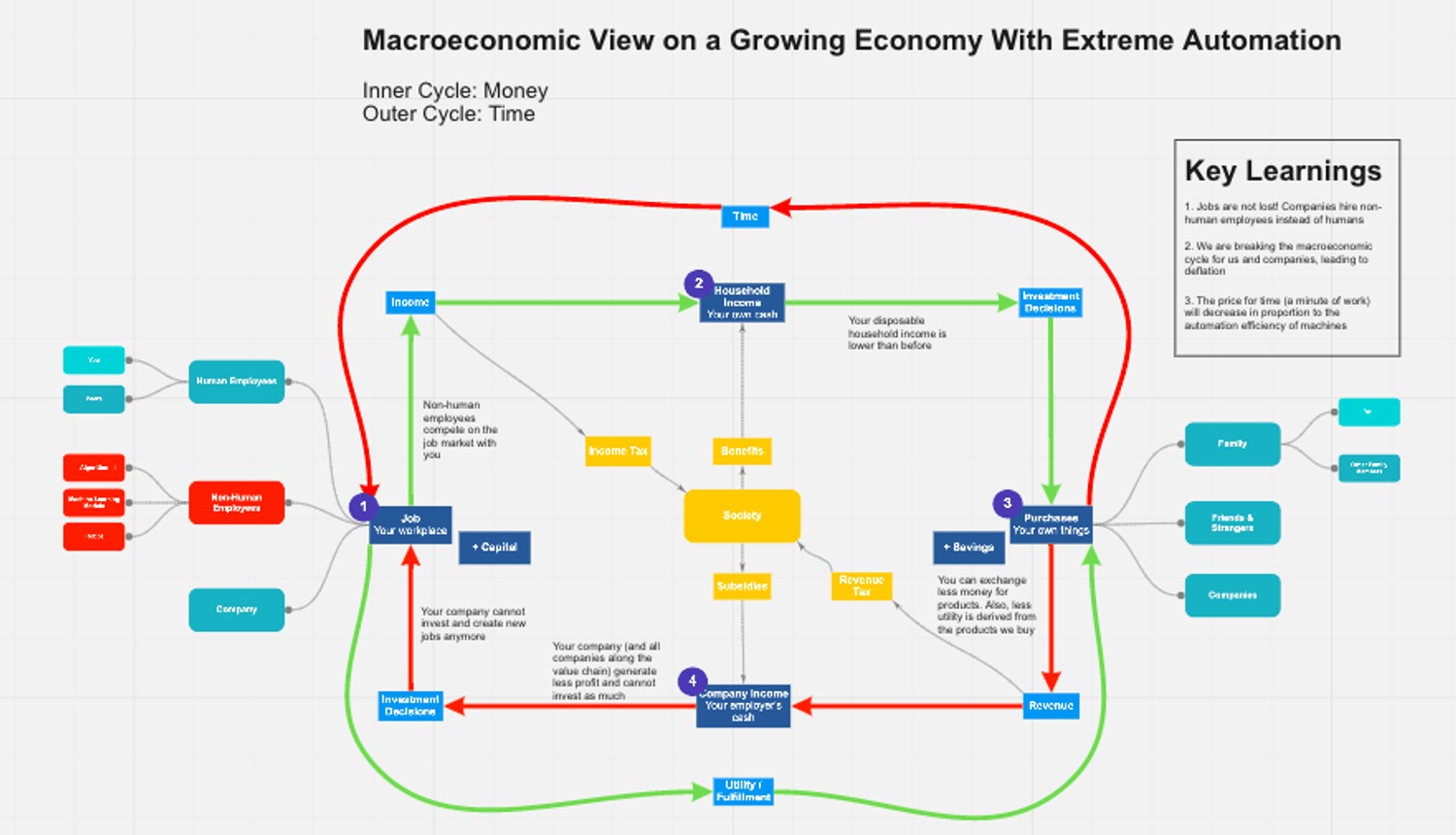
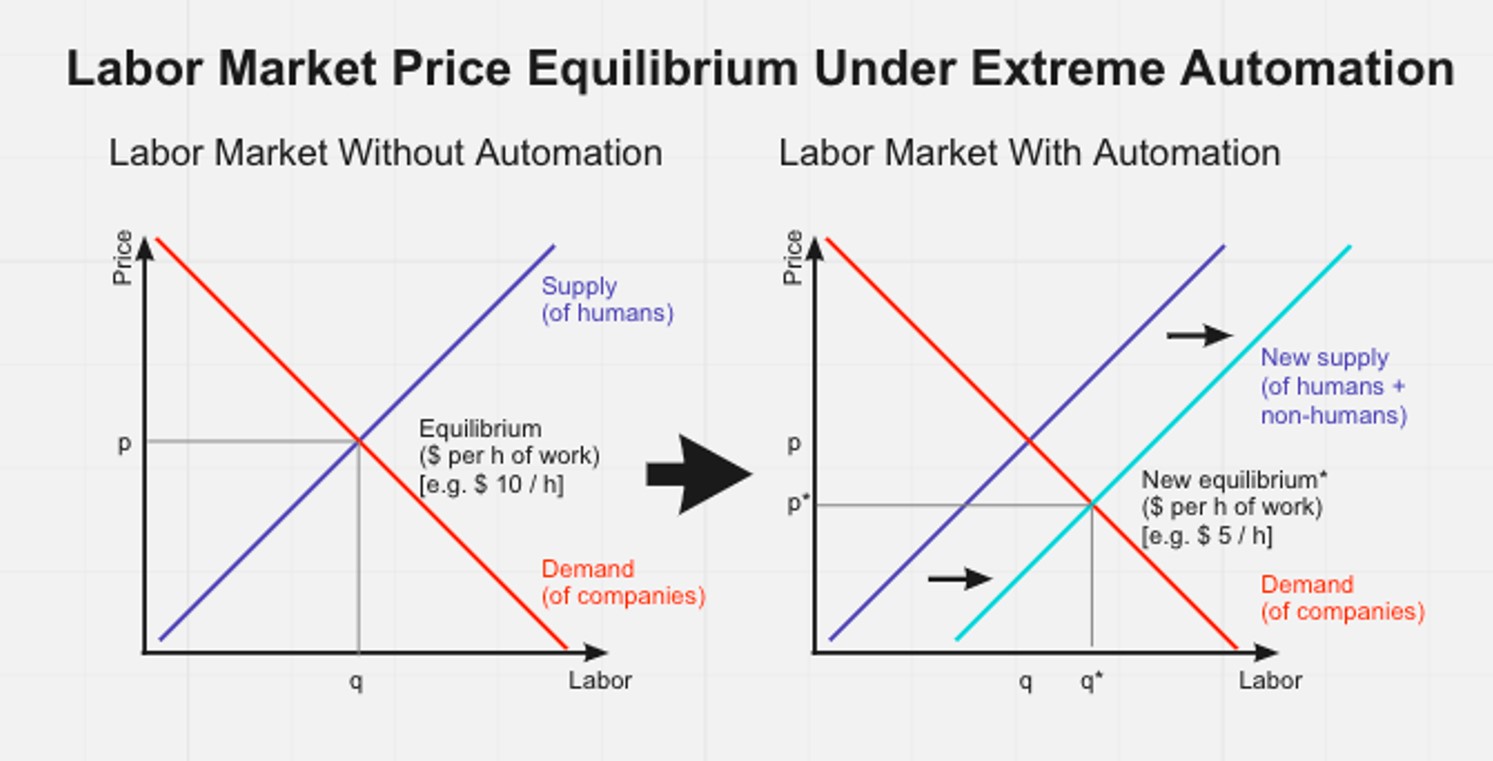

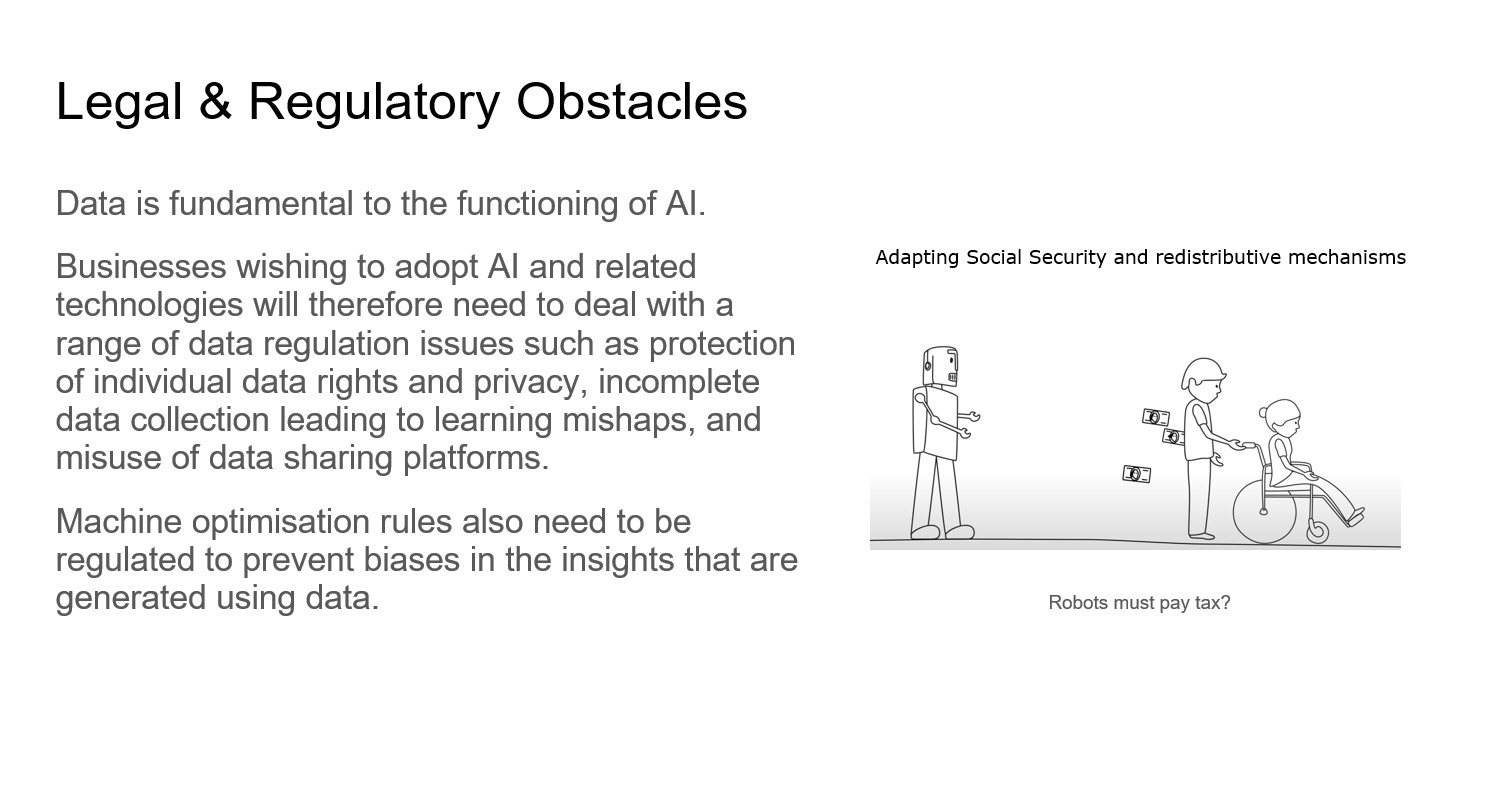
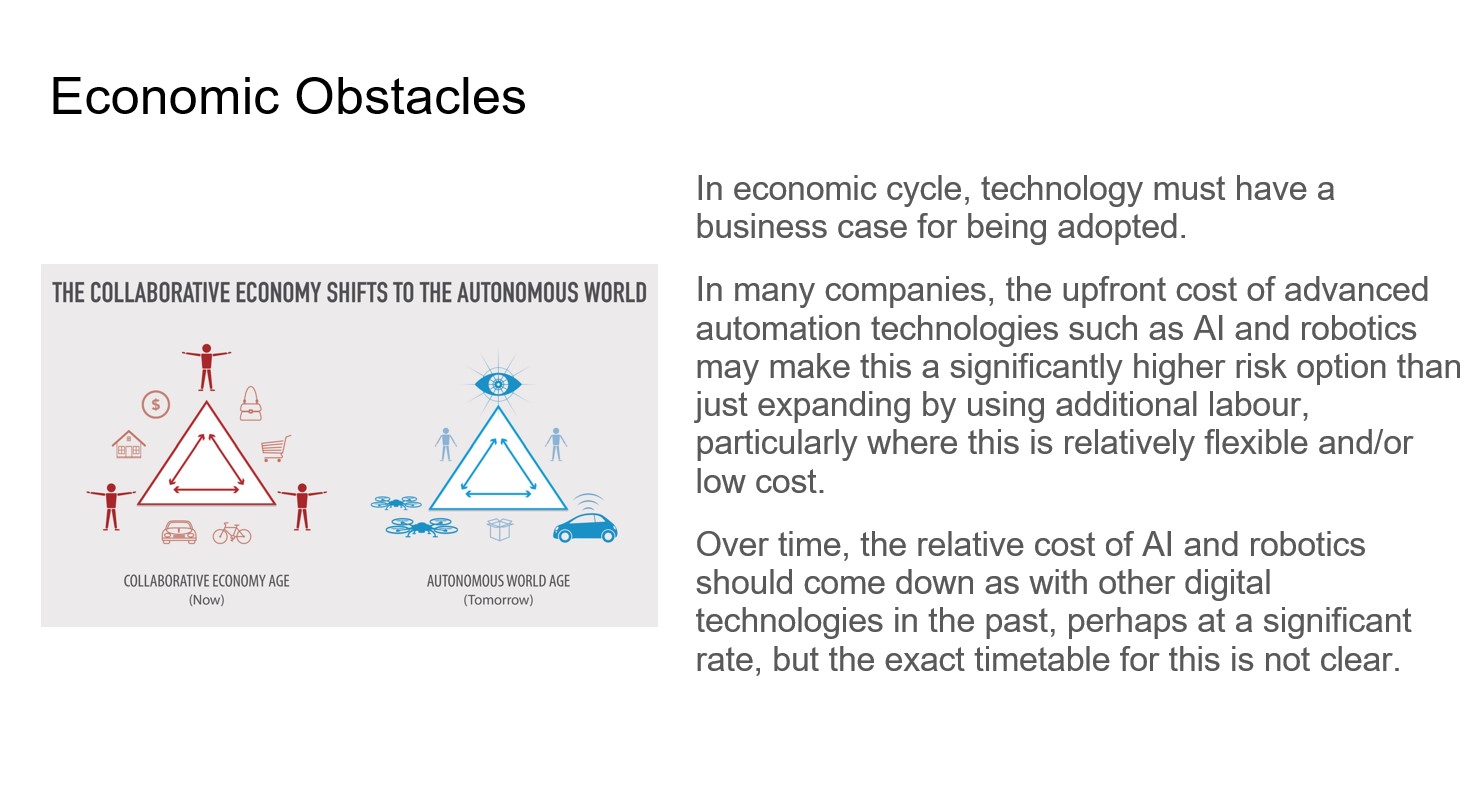





What I did
- Research
- Design
- Discussion
Rittel and Webber's 1973 formulation of wicked problems in social policy planning specified ten characteristics:
...
1. There is no definitive formulation of a wicked problem.
2. Wicked problems have no stopping rule.
3. Solutions to wicked problems are not true-or-false, but better or worse.
4. There is no immediate and no ultimate test of a solution to a wicked problem.
5. Every solution to a wicked problem is a "one-shot operation"; because there is no opportunity to learn by trial and error, every attempt counts significantly.
6. Wicked problems do not have an enumerable (or an exhaustively describable) set of potential solutions, nor is there a well-described set of permissible operations that may be incorporated into the plan.
7. Every wicked problem is essentially unique.
8. Every wicked problem can be considered to be a symptom of another problem.
9. The existence of a discrepancy representing a wicked problem can be explained in numerous ways. The choice of explanation determines the nature of the problem's resolution.
10. The social planner has no right to be wrong (i.e., planners are liable for the consequences of the actions they generate).
Conklin later generalized the concept of problem wickedness to areas other than planning and policy; Conklin's defining characteristics are:
1. The problem is not understood until after the formulation of a solution.
2. Wicked problems have no stopping rule.
3. Solutions to wicked problems are not right or wrong.
4. Every wicked problem is essentially novel and unique.
5. Every solution to a wicked problem is a "one shot operation."
6. Wicked problems have no given alternative solutions.
References
[1] Prettner, K. (2019). A note on the implications of automation for economic growth and the labor share. Macroeconomic Dynamics, 23(3), 1294-1301.
[2] Frey, C. B. (2019). Learning From Automation Anxiety of the Past. MIT Sloan Management Review. https://sloanreview. mit. edu/article/learning-from-automation-anxiety-ofthe-past.
[3] Landes, D. S. (2003). The unbound Prometheus: technological change and industrial development in Western Europe from 1750 to the present. Cambridge University Press.
[4] Hobsbawm, E. J. (1963). The standard of living during the Industrial Revolution: a discussion. The Economic History Review, 16(1), 119-134.
[5] Tsichritzis, D. (1997). The dynamics of innovation. In Beyond calculation (pp. 259-265). Springer, New York, NY.
[6] Johannessen, J. A. (2018). Automation, innovation and economic crisis: Surviving the fourth industrial revolution. Routledge.
[7] Lund, S., Madgavkar, A., Manyika, J., Smit, S., Ellingrud, K., Meaney, M., & Robinson, O. (2021). The future of work after COVID-19. McKinsey Global Institute, 18.
[8] Lambert, J. & Edward, C. (2021). How Robots Change the World. Oxford Economics.
[9] Manufacturing: NAICS 31-33 (2021). Industries at a Glance. US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Extracted on October 27, 2021 from https://www.bls.gov/iag/tgs/iag31-33.htm
[10] Lardinois, Frederic. How Amazon’s delivery robots will navigate your sidewalk. Techcrunch. Extracted on October 27, 2021 from https://techcrunch.com/2019/06/06/how-amazons-delivery-robots-will-navigate-your-sidewalk/
[11] Holmes, Aaron. Police robots keep malfunctioning, with mishaps ranging from running over a toddler's foot to ignoring people in distress. Businessinsider. Extracted on October 27, 2021 from https://www.businessinsider.com/police-robots-security-malfunctioning-fails-
knightscope-2020-1
[12] Reuters, Staff. Robot chef serves Chinese school dinners to lower COVID-19 risk. Reuters. Extracted on October 27, 2021 from https://www.reuters.com/article/health-coronavirus-
china-robot-chef/robot-chef-serves-chinese-school-dinners-to-lower-covid-19-risk-idUSKBN28B4ER
[13] Dizikes, Peter. How many jobs do robots really replace?. MIT News. Extracted on October 27, 2021 from https://news.mit.edu/2020/how-many-jobs-robots-replace-0504
[14] Ginni Rometty, Chairman, President, and CEO of IBM
[15] Semuels, Alana. Millions of Americans Have Lost Jobs in the Pandemic—And Robots and AI Are Replacing Them Faster Than Ever. Time. Extracted on October 27, 2021 from https://time.com/5876604/machines-jobs-coronavirus/